Gum Treatment Singapore: Restoring Your Gum Health
Information reviewed by: Dr Tay Chih Kien, B.D.S (Singapore) | Last updated: Jan 26, 2026
| Treatment | Gum Treatment |
| Purpose | To manage and treat gum disease, restore gum health, and preserve supporting structures of the teeth |
| Price |
|
| Treatment Duration | Several appointments depending on treatment type and severity |
| How to Book | Book via WhatsApp: 9667 1828 or Email: hello@truedental.sg |
| Clinic Location | 728 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 6, #01-4228, Singapore 560728 |
What Is Periodontal (Gum) Treatment?
Gum treatment refers to professional dental procedures aimed at managing and preventing gum
disease, improving gum health, and preserving the supporting structures of the teeth.
Treatment options vary based on the severity of the condition, ranging from non-surgical methods such as
deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) and antibacterial therapy to surgical procedures that restore
damaged gum tissue.
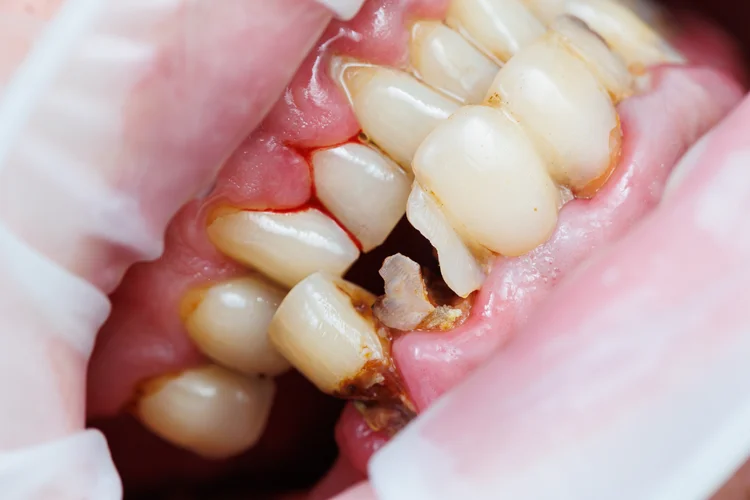
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection caused by plaque buildup along
the gumline. It begins as mild inflammation (gingivitis) and, if left untreated, can progress to
periodontitis, a more severe stage that leads to gum
recession, bone loss, and even tooth loss.
In Singapore, gum disease is highly prevalent. According to the 2019
National Adult Oral Health Survey (NAOHS), 77.6% of Singaporean adults were found to have some
form of periodontal disease. This highlights the importance of early detection and timely treatment to
prevent long-term oral health complications.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gum Disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by bacterial plaque buildup due to inadequate oral hygiene. However, several factors can increase the risk of developing gum disease, including:
- Poor Oral Hygiene – Inadequate or improper brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, leading to gum inflammation and infection.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use – Tobacco weakens the immune system, slows gum healing, and increases the risk of periodontitis, leading to faster gum deterioration and bone loss.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar weakens the immune system, making the gums more vulnerable to infection and slowing healing. Poorly controlled diabetes can worsen gum disease, while severe gum disease may further impact blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Changes – Fluctuations in hormones during pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can increase gum sensitivity and inflammation, making gums more reactive to plaque.
- Genetics – Genetic predisposition can influence an individual's immune response to oral bacteria, increasing susceptibility to gum disease even with good oral hygiene.
- Certain Medications – Anticoagulants, ACE inhibitors, and statins may increase the risk of periodontitis by affecting inflammation, blood flow, and immune response.
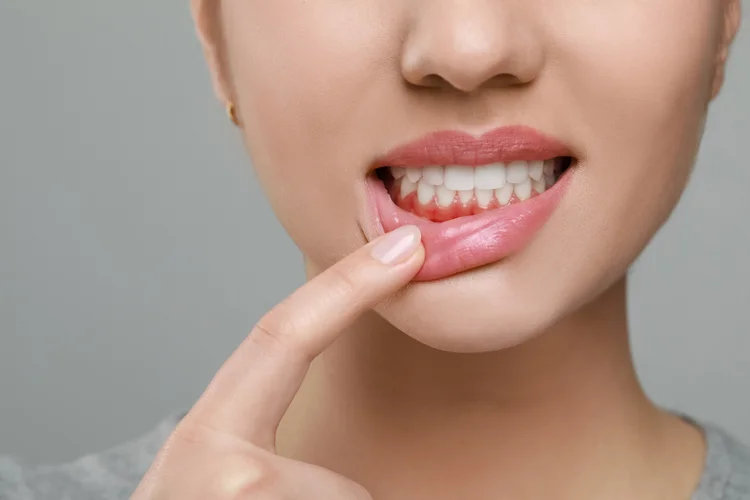

What Are Symptoms of Gum Disease?
Gum disease can cause a range of symptoms affecting oral health, which may worsen as the condition progresses. Common signs include:
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Receding gums, making teeth appear longer
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
Bleeding and inflammation are often the earliest signs, while gum recession, loose teeth, and pus typically indicate more advanced stages of gum disease.
Complications of Untreated Gum Disease
If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious oral health complications and may even affect overall health. Potential consequences include:
- Tooth Loss – Progressive bone loss and gum recession weaken the structures supporting the teeth, causing them to loosen and eventually fall out.
- Abscess Formation – Pockets of infection may develop in the gums, causing pain, swelling, and further tissue damage.
- Bone Deterioration – Severe periodontitis can erode the jawbone, affecting facial structure and the ability to support dental implants or prosthetics.
- Increased Risk of Systemic Diseases – Studies suggest that chronic inflammation from gum disease is linked to conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
WhatsApp Us Now
Types of Gum Disease Treatment
Treatment for gum disease depends on its severity and its impact on tooth and gum health, including risks such as gum recession and bone loss. Common treatment options include:
| Treatment | Description & Purpose | Severity Treated |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Surgical Treatment | ||
| Scaling and Polishing | Removes plaque, tartar, and surface stains from teeth to prevent gum inflammation and maintain oral hygiene. | Mild to moderate gum disease (gingivitis or early periodontitis). |
| Root Planing (Deep Cleaning) | Smoothen the root surfaces to prevent bacteria from reattaching and promote gum reattachment. | Early-stage periodontitis with gum detachment. |
| Antibacterial Therapy | Uses medicated mouthwashes, antibiotics, or antiseptic gels to reduce bacterial infection and inflammation. | Mild gum infections or as a complementary treatment. |
| Surgical Treatment | ||
| Gum Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery) | Lifts the gums to access and remove deep-seated plaque and tartar, then secures them back to reduce pocket depth. | Moderate to severe gum disease with deep periodontal pockets. |
| Gum Grafting | Uses tissue from another part of the mouth to cover exposed roots, helping to prevent further gum recession and reduce sensitivity. | Advanced periodontal disease resulting in gum recession. |
| Regenerative Procedures | Includes guided tissue regeneration or bone grafting to restore lost bone and gum tissue caused by severe gum disease. | Severe periodontitis with bone loss. |
In many cases, a combination of professional treatment and proper oral hygiene is required to effectively manage gum disease and prevent further progression.
Gum Treatment Cost in Singapore
At True Dental Studio, we offer a range of gum disease treatments at the following prices:
| Treatment | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | $27.25 to $65.40 |
| Scaling and Polishing | $49.05 to $174.40 |
| Root Planing | $163.50 to $272.50 per quadrant |
| Dental Bone Graft Surgery | From $2,000 |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
Eligible individuals may receive CHAS subsidies for
certain procedures. Additionally, some dental insurance plans may provide partial or full coverage
depending on your policy.
For more information on eligibility, claims, and coverage, please contact us, and our team will be happy to assist you.
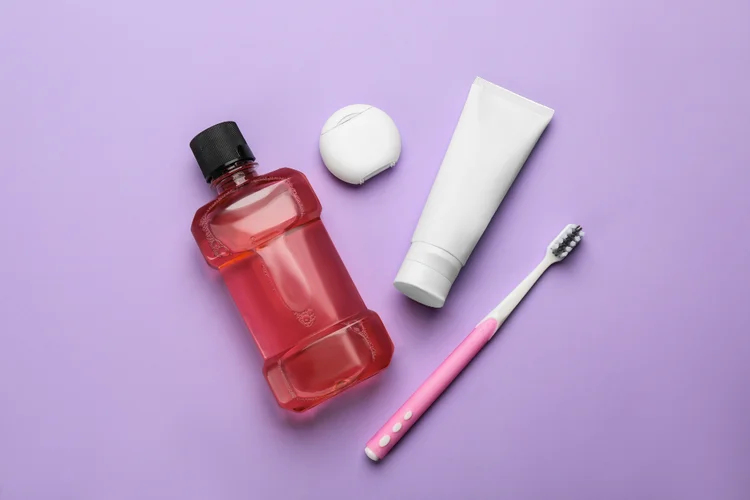
How to Prevent Gum Disease?
Maintaining good oral hygiene and adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease. Key preventive measures include:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and strengthen enamel.
- Floss daily to clean between teeth and along the gumline, where a toothbrush cannot reach.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacterial buildup and prevent gum inflammation when necessary.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and early detection of gum disease.
- Avoid smoking and tobacco products, as they weaken the immune system and increase gum disease risk.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C and calcium, to support gum health.

When to See a Dentist for Gum Treatment?
You should seek professional dental care if you experience persistent gum inflammation, bleeding, or
signs of gum recession. Other warning signs include chronic bad breath, loose teeth, increased tooth
sensitivity, or discomfort while eating and speaking.
If gum disease symptoms begin to interfere with your daily life or social interactions, such as avoiding
certain foods due to pain or feeling self-conscious about bad breath, it is important to seek treatment
promptly.
Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the need for more invasive
procedures.
Where to Get Gum Disease Treatment in Singapore?
Book Gum Treatment Appointment
Book NowEnquire More Through Email
Email Us NowEnquire More Through WhatsApp
WhatsApp Us NowWhy Choose True Dental Studio?
Friendly Dentist and Team
We treat every patient to the best of our ability. This is why families across Singapore have continued their dental care with us for years.
Minimal Discomfort
We are committed to keeping our patients as comfortable as possible, minimising any discomfort during treatment.
Affordable Treatments
We believe in pricing quality treatments at a competitive rate. We are transparent and upfront with our treatment costs.
Our Smile Scorecard
Frequently Asked Questions
At True Dental Studio, gum treatment prices start from $49.05 for scaling and polishing, $163.50 per quadrant for root planing. Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST but exclude consultation fees. CHAS subsidies and dental insurance may apply to eligible treatments. For detailed pricing, financing options, or subsidy eligibility, contact us directly.
Pus in the gums is treated by draining the abscess, deep cleaning to remove bacteria, and sometimes antibiotics to control infection. It usually results from advanced gum disease or a deep cavity. In severe cases, root canal treatment or gum surgery may be needed to prevent further damage. Seeking prompt dental care is crucial to stop the infection from spreading and protect the surrounding teeth and gums.
Antibiotics are sometimes prescribed for gum disease but cannot cure it alone. They are often used alongside treatments like scaling, root planing, or surgery to control bacterial infection and inflammation. However, they do not remove plaque or tartar, the main causes of gum disease. Long-term management requires good oral hygiene and regular dental care. A dentist can assess if antibiotics are needed based on your condition.
Non-surgical gum treatments focus on managing gum disease without invasive procedures. Common options include scaling and polishing, which removes plaque and tartar to prevent gum inflammation, and root planing (deep cleaning) to smooth root surfaces and encourage gum reattachment. Antibacterial therapy, such as medicated mouthwashes or topical antibiotics, may also be used to control infection. These treatments are most effective in the early stages of gum disease and should be complemented by proper oral hygiene.
Gum disease cannot be fully cured at home, but early-stage gingivitis can be managed with proper oral care. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and inflammation. A balanced diet and avoiding smoking also support gum health. However, once gum disease progresses to periodontitis, professional treatment is required to remove tartar buildup and restore gum health. Consulting a dentist can help determine the appropriate care for your condition.
Alcohol does not directly cause gum disease but increases the risk. It can lead to dry mouth, reduced saliva flow, and bacterial growth. Heavy drinking is linked to poor oral hygiene, weakened immunity, and gum inflammation. Sugary or acidic alcoholic drinks can further promote plaque buildup. While moderate consumption may have minimal impact, maintaining good oral hygiene and staying hydrated can help reduce potential risks.
If you have gum disease, seeking professional dental care is essential to prevent further progression. Early-stage gingivitis can often be reversed with improved oral hygiene and regular cleanings, while periodontitis may require deeper cleaning, antibacterial treatment, or surgery to restore gum health. Avoiding smoking, eating a balanced diet, and maintaining good oral hygiene can support recovery. Consulting a dentist can help determine the severity of your condition and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Gum disease is a common cause of bad breath due to bacterial buildup in deep gum pockets, which produces foul-smelling compounds. To manage bad breath from gum disease, professional treatment such as scaling and root planing is necessary to remove plaque and bacteria. Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help prevent further buildup. If bad breath persists, consult a dentist to address underlying gum disease effectively.
Gum disease itself does not directly cause a sore throat, but the bacteria from infected gums can spread, contributing to oral infections that may irritate the throat. Additionally, gum disease can cause pus formation and bad breath, which may lead to discomfort in the throat. If you experience persistent throat pain alongside gum inflammation, it is advisable to consult a dentist or doctor to rule out other infections or underlying conditions.
Sharing a toothbrush can increase the risk of transmitting bacteria that contribute to gum disease, cavities, and other oral infections. While gum disease itself is not contagious in the same way as a viral infection, harmful bacteria can spread through saliva. To prevent bacterial transmission, it is best to use your own toothbrush and replace it regularly. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding shared dental products can reduce the risk of gum problems.
Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, can often be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional cleanings. However, once it progresses to periodontitis, the damage to the gums and bone cannot be fully reversed but can be managed with professional treatments such as deep cleaning, antibacterial therapy, or surgery. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene are essential for preventing further progression. Consulting a dentist can help determine the best approach for your condition.
Signs of gum disease include bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, red or swollen gums, gum recession, and loose teeth. In early stages, symptoms may be mild, making regular dental check-ups essential for early detection. If left untreated, gum disease can progress to periodontitis, leading to more severe symptoms like pus formation and tooth loss. If you notice any symptoms, consulting a dentist promptly can help prevent further complications.
The duration of gum disease depends on its severity and how soon treatment is initiated. Gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral care and professional cleanings. However, periodontitis is a chronic condition that requires long-term management through deep cleaning, medication, or surgery to prevent further damage. Without treatment, gum disease can persist indefinitely and worsen over time, leading to irreversible damage to the gums and bone.
Toothpastes formulated for gum health, such as those containing fluoride, antibacterial agents, or anti-inflammatory ingredients, can help manage gum disease. Mouthwashes with chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride, or essential oils can reduce bacterial buildup and gum inflammation. However, these products should complement professional treatment rather than replace it. Consulting a dentist can help determine the most suitable toothpaste or mouthwash based on the severity of your gum condition.
The best way to prevent gum disease is through good oral hygiene and regular dental visits. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing to remove plaque between teeth, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help maintain healthy gums. Avoiding smoking, managing underlying health conditions like diabetes, and eating a balanced diet also play a role in gum health. Routine dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for early detection and prevention of gum disease.
The best treatment for gum repair depends on the severity of gum disease. Mild cases may be managed with professional cleanings, antibacterial therapy, and good oral hygiene. More advanced cases require treatments like root planing, gum grafting, or regenerative procedures to restore damaged tissues. Surgical options such as gum flap surgery may be necessary for deep pockets. Consulting a dentist can help determine the most appropriate treatment based on your condition.
The first stage of a gum infection is gingivitis, characterised by red, swollen gums that may bleed when brushing or flossing. This occurs due to plaque buildup along the gumline, leading to bacterial inflammation. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene and professional cleanings. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, which causes gum recession, bone loss, and potential tooth loss. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
The fastest way to heal gums is through professional dental care, including scaling and root planing to remove plaque and bacteria. Practicing good oral hygiene, such as brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash, helps reduce inflammation. Avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins C and D can also support gum healing. If symptoms persist, consulting a dentist ensures appropriate treatment for faster recovery.
There is no universal "stage 5" classification for gum disease, but the most advanced stage of periodontitis involves severe gum recession, significant bone loss, loose or shifting teeth, and possible tooth loss. At this stage, extensive treatment such as bone grafting, gum grafting, or tooth extractions followed by implants or dentures may be required. Managing advanced gum disease requires a combination of professional intervention and ongoing oral hygiene care.
Gum treatment is essential for preventing further damage to your teeth, gums, and jawbone. Treating gum disease early can prevent complications such as tooth loss, abscesses, and even systemic health risks linked to chronic inflammation. While costs vary depending on the severity of the condition, early intervention is often more affordable and less invasive than advanced treatments. Consulting a dentist can help assess your gum health and recommend necessary treatments for long-term oral well-being.
The discomfort level of gum treatment depends on the procedure and individual pain tolerance. Scaling and root planing may cause mild sensitivity, while surgical treatments like gum grafting or flap surgery can result in temporary soreness, usually managed with pain relievers. Local anaesthesia is typically used during procedures to minimise discomfort. Most post-treatment sensitivity usually subsides within a few days. Consulting a dentist can provide guidance on pain management and recovery expectations.
Gums cannot fully regenerate naturally once significant recession or bone loss has occurred. While mild gum inflammation (gingivitis) can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional cleanings, advanced gum disease (periodontitis) typically requires treatment. In severe cases, surgical restorative procedures like gum grafting, guided tissue regeneration, or bone grafting may be necessary to restore lost gum and bone tissue. Consulting a dentist can help determine the most suitable treatment for your condition.
Gum infections do not heal on their own and may worsen without treatment. If left untreated, infections can spread, leading to abscess formation, gum recession, and bone loss. Professional treatment, such as deep cleaning, antibiotics, or surgical intervention, may be required to control the infection and prevent further damage. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking prompt dental care are essential for managing gum infections effectively.
The cost of gum repair varies based on the severity of the condition and required treatment. At True Dental Studio, prices start from $49.05 for scaling and polishing, $163.50 per quadrant for root planing, and $2,000 onwards for dental bone graft surgery. Surgical procedures like gum grafting or bone grafting are generally more costly. CHAS subsidies and dental insurance may help offset some expenses. Contact us for details on pricing, services, and financing options.
